Deepfake technology is reshaping how we perceive digital content, blending reality and fiction in innovative and concerning ways. Understanding the mechanics behind this technology and the measures to counteract its misuse can help us navigate the digital landscape more effectively.
Understanding DeepFake Technology
Deepfake technology uses specialized algorithms to create convincing fake images, videos, and audio. The process involves two key components: a generator and a discriminator.
The generator creates an initial set of fake content based on training data. The discriminator then analyzes this content, identifying imperfections. This feedback loop continues until the output is highly realistic.
These algorithms form a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). GANs use deep learning to recognize patterns in real images and apply them to fabricate fakes. To create a deepfake video, a GAN analyzes the subject from various angles, assessing behavior, movement, and speech patterns.
Methods to create deepfakes include:
- Source video manipulation
- Face swapping
- Audio cloning
- Lip-syncing technology
Deepfakes depend on technologies such as:
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for facial recognition
- Autoencoders for capturing and imposing attributes
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms for producing fake audio
- High-performance computing for necessary computational power
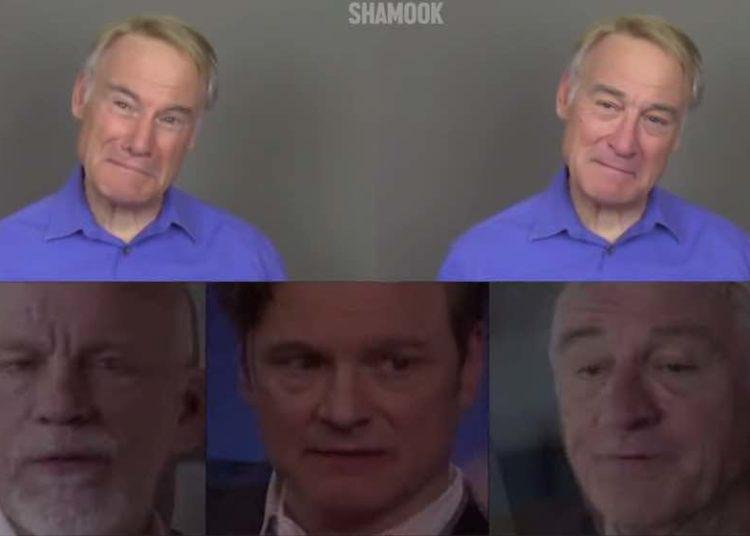

Applications and Risks of DeepFakes
Deepfake technology has applications across various domains, presenting both opportunities and risks:
Positive Applications:
- Entertainment: seamless visual effects and realistic character dialogues
- Customer support: AI-driven caller response services
- Education: personalized AI tutors
Potential Risks:
- Misinformation: Eroding public trust and fueling political tensions
- Blackmail and Reputational Damage: Placing individuals in compromising situations
- Fraud: Falsely authenticating someone's identity
- Cybersecurity Threats: Bypassing security measures or gaining unauthorized access
Addressing these risks requires both technological intervention and increased awareness. People need to be informed about the signs of deepfakes and equipped with tools to verify content authenticity.

Adobe's Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI)
Adobe's Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI) aims to establish a standard for verifying the authenticity of digital content. The CAI's primary tool is "Content Credentials," metadata that includes creator identity, device details, and edit history.
Cryptographic asset hashing is the core technology behind Content Credentials. This generates unique digital fingerprints for content, ensuring that any tampering can be detected.
The CAI is a collaborative effort involving over 300 organizations, including tech companies, media entities, and camera manufacturers. This coalition ensures a cross-industry approach to tackling misinformation.
Practical applications of the CAI include:
- Leica's new M 11-P camera, incorporating Content Credentials at the moment of capture
- Qualcomm's Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 chip, extending similar technology to smartphones
- TikTok implementing Content Credentials to label AI-generated content
The success of the CAI also depends on educating consumers about how to use these tools to verify content authenticity.
Content Credentials in Action
Leica's M 11-P camera and Qualcomm's Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 chip demonstrate how Content Credentials are being integrated into devices. This integration ensures that digital media carries a verifiable history from the moment of capture.
Content Credentials are also being applied in platforms like LinkedIn, aiding in preserving the integrity of professional content. This helps combat misinformation and enhances credibility within professional networks.
"Transparency is the key to trustworthy content," – Dana Rao, General Counsel and Chief Trust Officer at Adobe
As more devices and services incorporate this technology, content authentication could become a standard feature in our digital experience. This shift has the potential to improve public trust in digital media and encourage responsible media consumption.
The adoption of Content Credentials by social platforms like TikTok illustrates the impact such technology can have on enhancing transparency and setting industry standards. As this trend continues, we may see a broader implementation of content verification tools across various media channels, leading to a more secure and credible information ecosystem.
Legislation and Policy Efforts
Legislation and policy efforts are vital components in combating the threats posed by deepfake technology. Several legislative initiatives are in progress:
- The Deepfake Task Force Act aims to establish a National Deepfake and Digital Provenance task force. This task force would focus on developing digital provenance standards to verify online information's authenticity and reduce disinformation spread.
- The DEFIANCE Act (Disrupt Explicit Forged Images and Non-Consensual Edits) would enable victims to pursue legal action against deepfake creators who recklessly disregarded consent. This legislation is crucial for combating non-consensual deepfake pornography.
- The Preventing Deepfakes of Intimate Images Act seeks to criminalize the non-consensual sharing of deepfakes related to intimate images.
- The Take It Down Act aims to facilitate the swift removal of revenge porn from online platforms.
- The Deepfakes Accountability Act mandates creators to digitally watermark deepfake content, emphasizing transparency and making it a crime to fail to identify potentially harmful deepfakes.
These legislative efforts, combined with technological solutions like Adobe's Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI) and educational initiatives, form a comprehensive strategy to address the issues posed by deepfakes. Together, they create a defense against the spread of disinformation and the abuse of deepfake technology.

Future of Content Authenticity
The future of content authenticity technologies holds promising prospects in AI detection tools and industry-wide standards.
Advancements in AI Detection Tools
Future AI detection tools could potentially operate in real-time, analyzing videos and images instantly to flag alterations. This enhancement would strengthen our ability to intercept misinformation quickly.
Industry-Wide Standards
Establishing industry-wide standards will be critical in ensuring consistent application and effectiveness of content authentication across platforms and devices. This would require collaboration across tech companies, media organizations, and regulatory bodies.
Public Education
Public education remains essential in combating misinformation. Comprehensive digital literacy programs could be embedded in school curriculums and public awareness campaigns, focusing on:
- Media evaluation principles
- Critical thinking skills
- Understanding deepfake technology and its risks
Interactive Platforms
Interactive platforms could engage the public in understanding deepfake technology. For example, educational apps could simulate scenarios involving deepfake detection, allowing users to practice identifying manipulated content.
Continuous Dialogue
Continuous dialogue between the public and technology developers will be imperative. Feedback mechanisms should be established to adapt and improve content authenticity tools based on user experiences and concerns.
The future of content authenticity relies on a holistic approach that integrates technology, policy, and public engagement to uphold the integrity of digital information in a rapidly changing landscape.
In the ongoing battle against misinformation, combining technological solutions with public awareness is key. Fostering a culture of transparency and authenticity in digital media will be crucial in maintaining trust and integrity.
"Transparency is the key to trustworthy content."
As we move forward, it's essential to remember that the fight against deepfakes and misinformation is not solely a technological challenge, but a societal one that requires collective effort and vigilance.




